Obsessive is a LIMITATION of the RED personality in the Color Code Personality Assessment.
Obsessive
"Compulsiveness is like darkness – you cannot fight with it. You have to turn on the light of consciousness."― Sadhguru
Lisa Ulshafer /  Are you constantly caught up in a cycle of overthinking and can't seem to let things go? Do you find yourself getting lost in the details and forgetting the bigger picture? Obsessive behavior is a pattern of thinking or acting that involves excessive preoccupation with a particular thought, idea, or behavior. It is characterized by persistent and intrusive thoughts, urges, or impulses that are difficult to control, often resulting in repetitive behaviors or rituals.
Are you constantly caught up in a cycle of overthinking and can't seem to let things go? Do you find yourself getting lost in the details and forgetting the bigger picture? Obsessive behavior is a pattern of thinking or acting that involves excessive preoccupation with a particular thought, idea, or behavior. It is characterized by persistent and intrusive thoughts, urges, or impulses that are difficult to control, often resulting in repetitive behaviors or rituals.
Obsession can manifest in various areas of life, such as relationships, work, health, or personal interests. It may arise from a deep-seated need for control, fear of uncertainty, or a desire for perfection. Obsessive behavior can impact one's daily functioning, emotional well-being, and relationships, and may be accompanied by anxiety, stress, or distress. It is a complex psychological phenomenon that can have both positive and negative effects, depending on the context and severity of the obsession.
Here are some common signs that you may be obsessive:
-
Persistent and intrusive thoughts: You find yourself having recurrent and unwanted thoughts, ideas, or urges that are difficult to dismiss or ignore, and they may interfere with your ability to focus on other tasks.
-
Repetitive behaviors or rituals: You engage in repetitive behaviors, routines, or rituals in an attempt to alleviate anxiety or distress, even if they seem excessive or unnecessary.
-
Excessive need for control: You feel a strong urge to control certain aspects of your life or environment, and you may have difficulty letting go of control, even in situations where it may not be necessary or appropriate.
-
Perfectionism: You have a strong desire for things to be perfect and may engage in excessive checking, arranging, or organizing behaviors to ensure that things are done exactly as you envision them.
-
Difficulty tolerating uncertainty: You have a low tolerance for ambiguity or uncertainty, and you may feel compelled to seek reassurance or engage in repetitive behaviors to reduce uncertainty or anxiety.
-
Interference with daily functioning: Your obsessive thoughts or behaviors may interfere with your ability to perform daily activities, such as work, school, or social interactions, and may consume a significant amount of your time and energy.
-
Emotional distress: You may experience heightened levels of anxiety, stress, or distress as a result of your obsessive thoughts or behaviors, and may feel powerless or distressed by their impact on your life.
-
Impact on relationships: Your obsessions may affect your relationships with others, as you may have difficulty trusting or relying on others, or may struggle with interpersonal conflicts related to your obsessive behaviors.
-
Difficulty adapting to change: You may have difficulty adapting to changes or disruptions in your routine or environment, and may experience increased distress or anxiety in response to unexpected or unplanned events.
-
Awareness of the excessive nature of thoughts or behaviors: You may recognize that your thoughts or behaviors are excessive or irrational, but feel unable to control or stop them.
Here are 9 strategies for overcoming being obsessive:
-
Challenge and reframe thoughts: Learn to identify and challenge irrational or excessive thoughts that contribute to obsessive behavior. Practice reframing them in a more realistic and balanced way, replacing negative or intrusive thoughts with more positive and constructive ones.
-
Practice mindfulness: Mindfulness techniques, such as meditation, deep breathing, and grounding exercises, can help you become more aware of the present moment without judgment, and reduce the intensity of obsessive thoughts and urges.
-
Gradual exposure and response prevention (ERP): ERP is a type of cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) commonly used to treat obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD). It involves gradually exposing yourself to the source of your obsession while refraining from engaging in the usual compulsive behaviors, with the guidance of a therapist.
-
Develop healthy coping mechanisms: Identify healthy coping mechanisms, such as engaging in physical exercise, practicing relaxation techniques, or talking to a trusted friend or family member, to manage anxiety or distress associated with obsessive thoughts or behaviors.
-
Create a structured routine: Establishing a structured daily routine can help reduce uncertainty and increase a sense of control, which can be particularly helpful for those struggling with obsessive tendencies.
-
Practice self-care: Take care of yourself physically, emotionally, and mentally. Get enough sleep, eat balanced meals, engage in activities that you enjoy, and prioritize self-care activities that promote relaxation and stress reduction.
-
Practice self-compassion: Be kind and compassionate to yourself, and practice self-acceptance. Acknowledge that nobody is perfect, and it's okay to make mistakes or have imperfections.
-
Challenge avoidance behaviors: Avoidance behaviors can reinforce obsessive thoughts and behaviors. Gradually face and confront situations or triggers that typically trigger your obsessions to learn to tolerate uncertainty and reduce the need for compulsive behaviors.
-
Build a support system: Surround yourself with supportive and understanding individuals who can provide encouragement, understanding, and guidance as you work towards overcoming obsessive behavior.
Overcoming obsessive behavior allows for greater flexibility, spontaneity, and adaptability in navigating daily challenges and uncertainties. By freeing yourself of being burdened by intrusive thoughts and excessive behaviors, you can engage in healthier coping mechanisms, build stronger relationships, and enjoy a more balanced and fulfilling lifestyle. You can focus on what truly matters to you, without being consumed by obsessions or compulsions. Letting go of obsessive tendencies can lead to improved emotional well-being, increased self-acceptance, and a greater sense of freedom and peace of mind. It may require effort and support, but the journey towards overcoming obsessive behavior can open up new possibilities for a more vibrant and fulfilling life.
Obsessive
― Sadhguru
 Are you constantly caught up in a cycle of overthinking and can't seem to let things go? Do you find yourself getting lost in the details and forgetting the bigger picture? Obsessive behavior is a pattern of thinking or acting that involves excessive preoccupation with a particular thought, idea, or behavior. It is characterized by persistent and intrusive thoughts, urges, or impulses that are difficult to control, often resulting in repetitive behaviors or rituals.
Are you constantly caught up in a cycle of overthinking and can't seem to let things go? Do you find yourself getting lost in the details and forgetting the bigger picture? Obsessive behavior is a pattern of thinking or acting that involves excessive preoccupation with a particular thought, idea, or behavior. It is characterized by persistent and intrusive thoughts, urges, or impulses that are difficult to control, often resulting in repetitive behaviors or rituals.
Obsession can manifest in various areas of life, such as relationships, work, health, or personal interests. It may arise from a deep-seated need for control, fear of uncertainty, or a desire for perfection. Obsessive behavior can impact one's daily functioning, emotional well-being, and relationships, and may be accompanied by anxiety, stress, or distress. It is a complex psychological phenomenon that can have both positive and negative effects, depending on the context and severity of the obsession.
Here are some common signs that you may be obsessive:
-
Persistent and intrusive thoughts: You find yourself having recurrent and unwanted thoughts, ideas, or urges that are difficult to dismiss or ignore, and they may interfere with your ability to focus on other tasks.
-
Repetitive behaviors or rituals: You engage in repetitive behaviors, routines, or rituals in an attempt to alleviate anxiety or distress, even if they seem excessive or unnecessary.
-
Excessive need for control: You feel a strong urge to control certain aspects of your life or environment, and you may have difficulty letting go of control, even in situations where it may not be necessary or appropriate.
-
Perfectionism: You have a strong desire for things to be perfect and may engage in excessive checking, arranging, or organizing behaviors to ensure that things are done exactly as you envision them.
-
Difficulty tolerating uncertainty: You have a low tolerance for ambiguity or uncertainty, and you may feel compelled to seek reassurance or engage in repetitive behaviors to reduce uncertainty or anxiety.
-
Interference with daily functioning: Your obsessive thoughts or behaviors may interfere with your ability to perform daily activities, such as work, school, or social interactions, and may consume a significant amount of your time and energy.
-
Emotional distress: You may experience heightened levels of anxiety, stress, or distress as a result of your obsessive thoughts or behaviors, and may feel powerless or distressed by their impact on your life.
-
Impact on relationships: Your obsessions may affect your relationships with others, as you may have difficulty trusting or relying on others, or may struggle with interpersonal conflicts related to your obsessive behaviors.
-
Difficulty adapting to change: You may have difficulty adapting to changes or disruptions in your routine or environment, and may experience increased distress or anxiety in response to unexpected or unplanned events.
-
Awareness of the excessive nature of thoughts or behaviors: You may recognize that your thoughts or behaviors are excessive or irrational, but feel unable to control or stop them.
Here are 9 strategies for overcoming being obsessive:
-
Challenge and reframe thoughts: Learn to identify and challenge irrational or excessive thoughts that contribute to obsessive behavior. Practice reframing them in a more realistic and balanced way, replacing negative or intrusive thoughts with more positive and constructive ones.
-
Practice mindfulness: Mindfulness techniques, such as meditation, deep breathing, and grounding exercises, can help you become more aware of the present moment without judgment, and reduce the intensity of obsessive thoughts and urges.
-
Gradual exposure and response prevention (ERP): ERP is a type of cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) commonly used to treat obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD). It involves gradually exposing yourself to the source of your obsession while refraining from engaging in the usual compulsive behaviors, with the guidance of a therapist.
-
Develop healthy coping mechanisms: Identify healthy coping mechanisms, such as engaging in physical exercise, practicing relaxation techniques, or talking to a trusted friend or family member, to manage anxiety or distress associated with obsessive thoughts or behaviors.
-
Create a structured routine: Establishing a structured daily routine can help reduce uncertainty and increase a sense of control, which can be particularly helpful for those struggling with obsessive tendencies.
-
Practice self-care: Take care of yourself physically, emotionally, and mentally. Get enough sleep, eat balanced meals, engage in activities that you enjoy, and prioritize self-care activities that promote relaxation and stress reduction.
-
Practice self-compassion: Be kind and compassionate to yourself, and practice self-acceptance. Acknowledge that nobody is perfect, and it's okay to make mistakes or have imperfections.
-
Challenge avoidance behaviors: Avoidance behaviors can reinforce obsessive thoughts and behaviors. Gradually face and confront situations or triggers that typically trigger your obsessions to learn to tolerate uncertainty and reduce the need for compulsive behaviors.
-
Build a support system: Surround yourself with supportive and understanding individuals who can provide encouragement, understanding, and guidance as you work towards overcoming obsessive behavior.
Overcoming obsessive behavior allows for greater flexibility, spontaneity, and adaptability in navigating daily challenges and uncertainties. By freeing yourself of being burdened by intrusive thoughts and excessive behaviors, you can engage in healthier coping mechanisms, build stronger relationships, and enjoy a more balanced and fulfilling lifestyle. You can focus on what truly matters to you, without being consumed by obsessions or compulsions. Letting go of obsessive tendencies can lead to improved emotional well-being, increased self-acceptance, and a greater sense of freedom and peace of mind. It may require effort and support, but the journey towards overcoming obsessive behavior can open up new possibilities for a more vibrant and fulfilling life.
Change can be challenging and difficult to do all on your own.
Contact Lisa today to make the kind of changes in your life that lift you to your greatest potential.

2 Free Template Downloads
#1. Developing Strengths & Becoming Charactered
#2. Removing My Limitations
Fill out the form below to receive your free templates:
Click to explore the Strengths & Limitations of each color:
FULL Analysis
A completely customized report that is designed to fully analyze your personality and provide bonus tools to help you on your way to personal development.
Results Include:
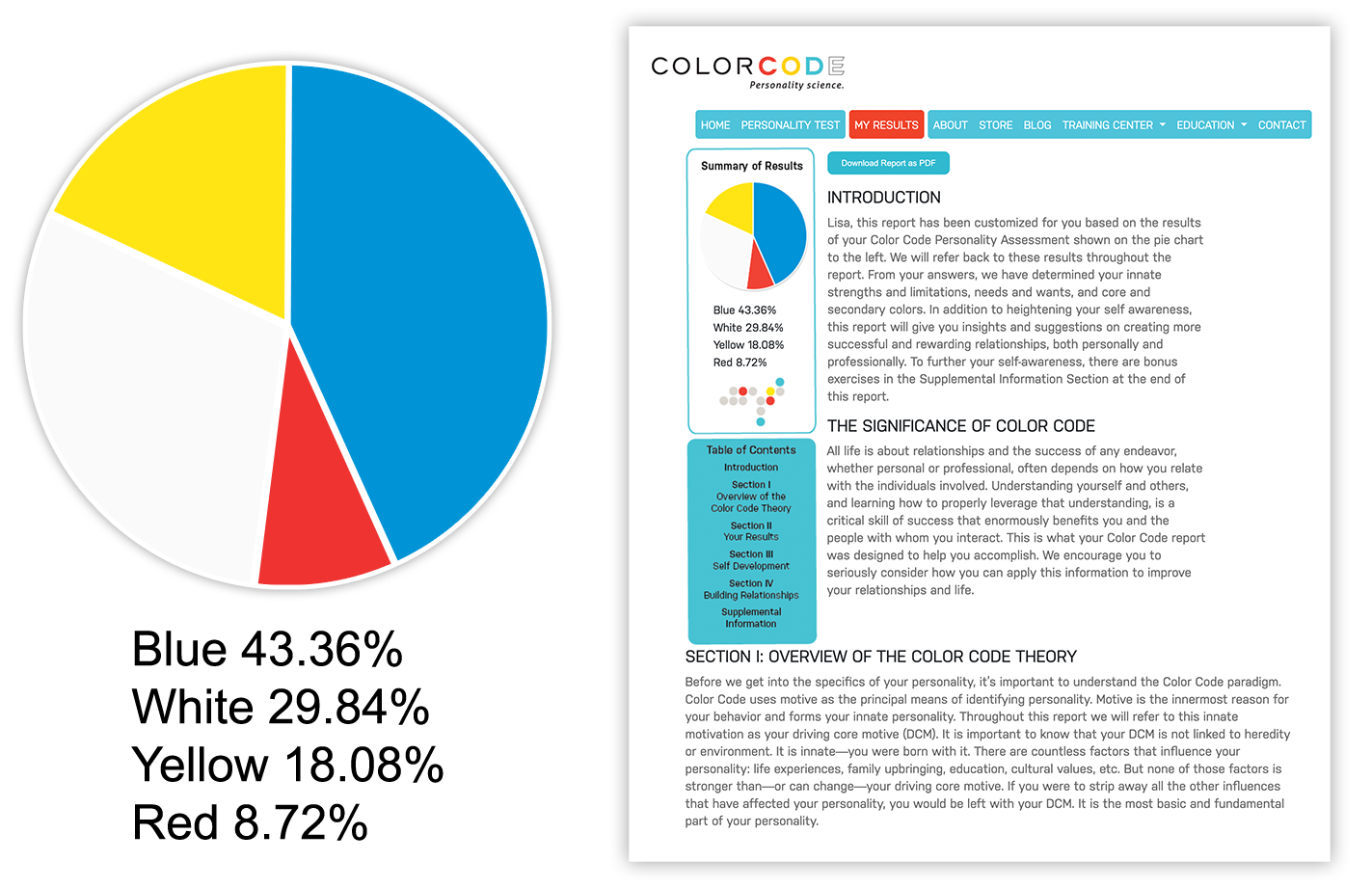
- Pie chart showing you what you scored in all 4 colors.
- Comprehensive analysis containing 35+ page report with customized content that describes your individual personality style in depth.
- List of your innate strengths and limitations.
- A breakdown of secondary colors and how they affect your personality.
- Throughout are videos, activities and other tools embedded to help you more fully understand your results.